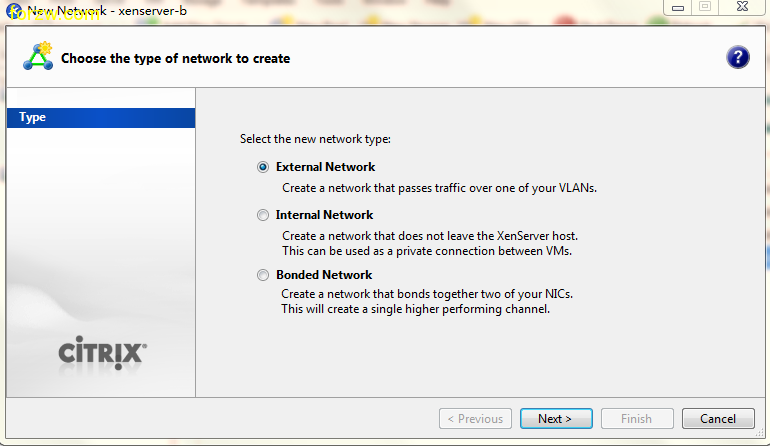
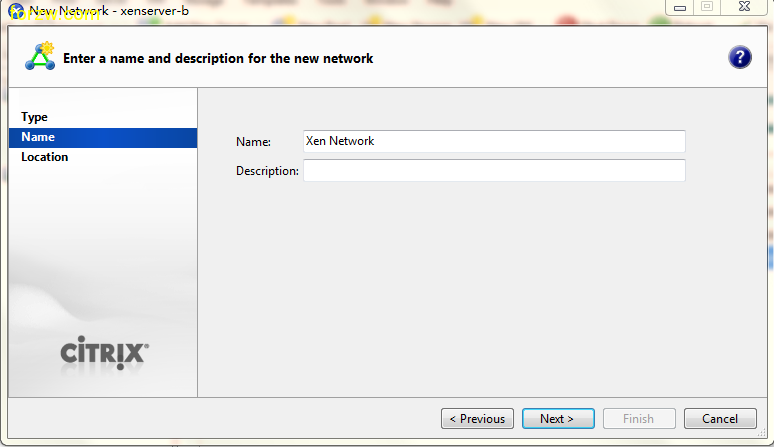
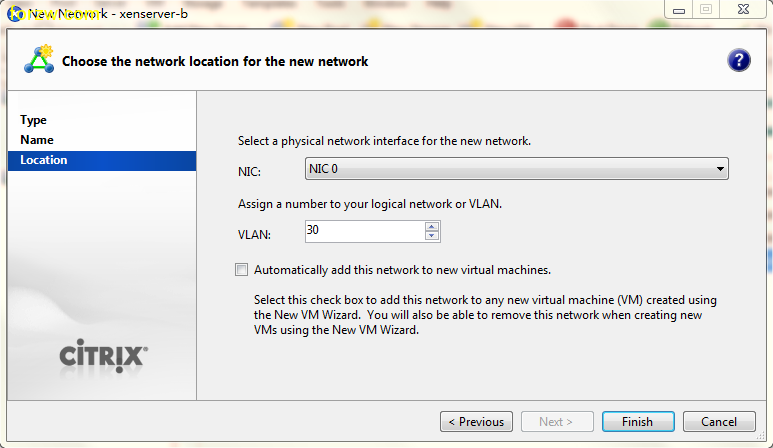
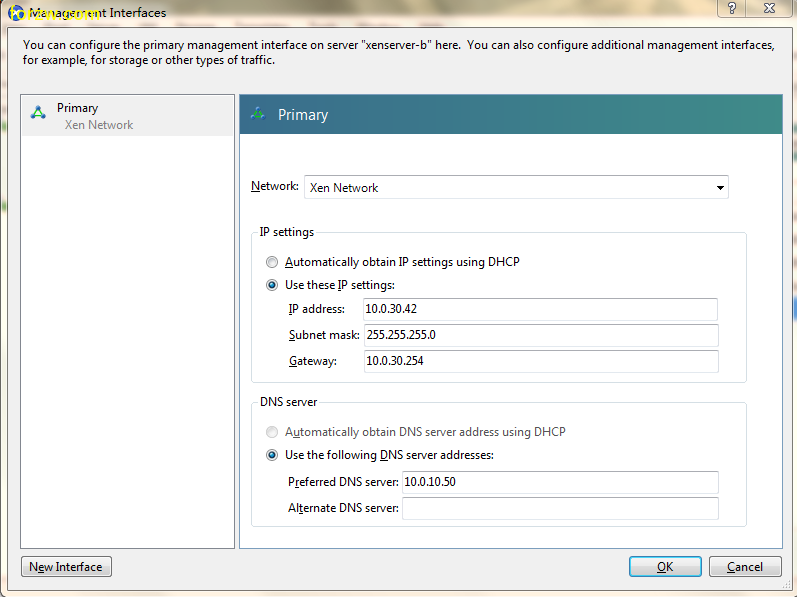
how-to activate SSH in ESXi
When you firs install ESXi Server (the installable version), by default the service ssh is desactivated. Tech Support
Mode provides a command-line interface that can be used to diagnose and repair ESX Server 3i hosts. But it is possible very
easy to activate SSH. Here is how:
Requirements:
You have to have direct access to console
1.) While you are at the console hit ALT + F1
2.) Type in ” unsupported ” and hit Enter
3.) Go ahead and type the root password
4.) Go and edit the /etc/inetd.conf file
5.) Uncoment the line where you can see “#ssh” (line 32). Remove the “#” mark at the begining.
6.) Type “ps -a |grep inetd”
7.) Kill the process
8.) start inetd
Remarque: In case that this don’t work. It means that when you type ”
unsupported ” nothing happens, you’ll have to follow this:
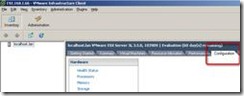
1.) Open the VI client, click onto the ESXi server you want to manage and go to Configuration TAB
Remarque: In case that this don’t work. It means that when you type ” unsupported ” nothing happens, you’ll have to follow this:
1.) Open the VI client, click onto the ESXi server you want to manage and go to Configuration TAB
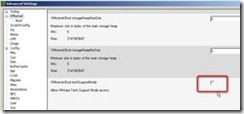
3.) Uncheck the VMkernel.boot.techSupportMode
4.) Reboot the ESXi Server. Before restarting the host, you should shut down virtual machines on that host